Osteochondrosis -degenerative-dystrophic damage to the tissues of the spine, characterized by damage to the intervertebral discs, adjacent joint surfaces and vertebral bodies, the ligament apparatus of the spine.
Most often, the pathological processes in osteochondrosis first affect the bones and ligaments. The fact that the disease has already begun, we usually learn when complications occur - pain, sensory disturbances, muscle atrophy, dysfunction of internal organs.
Who suffers from osteochondrosis?
Today, 40 to 90% of the world's population suffers from osteochondrosis. The disease most often affects people over the age of 30. However, the first symptoms of osteochondrosis may appear in adolescence.
Stages of development of osteochondrosis of the spine
- The first stage of the development of osteochondrosis.
Dehydration of the nucleus pulposus begins. This reduces the height of the disc. Cracks appear in the annular fibrosis, but the pathological process does not extend beyond the intervertebral disc.
- The second stage of the development of osteochondrosis.
As a result of the reduction in the height of the disc, the points of attachment of the muscles and the ligaments belonging to two adjacent vertebrae converge. Therefore, muscles and ligaments sag. This can lead to excessive mobility of the two vertebrae relative to each other, ie instability of the spinal motor segment is formed. This stage is characterized by sliding or displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other with the formation of spondylolisthesis.
- The third stage in the development of osteochondrosis.
During this period, the most pronounced morphological changes occur, which primarily affect the intervertebral discs themselves: prolapses and protrusions of discs are formed. The joint apparatus of the spinal-motor segment also suffers. Subluxations occur in the intervertebral joints and non-vertebral joints, arthrosis is formed.
- The fourth stage of the development of osteochondrosis.
At this stage, adaptive changes occur in the affected segments of the spine. The body tries to overcome the excessive mobility of the vertebrae, to immobilize the spine to maintain its supporting and protective functions. In this regard, marginal bone growths appear on the adjacent surfaces of the vertebral bodies, in other words, osteophytes. An osteophyte that grows "in the wrong place" causes microtrauma to the nerve root. In the fourth stage, the processes of fibrous ankylosis usually begin in the intervertebral discs and joints. In the end, the vertebromotor segment turns out to be walled up in a shell - the clinical manifestations subside.
Causes of osteochondrosis
In each of the many existing theories for the development of osteochondrosis, various causes are responsible for the onset of the disease, such as mechanical damage, hereditary predisposition or metabolic disorders. Particular difficulty in determining the cause of osteochondrosis is due to the fact that this disease can occur in both older people and young people, both physically fit and less trained. It is widely believed that the cause of osteochondrosis is the deposition of salts in the spine: it is claimed that on X-rays the salt can be seen in the form of "growths" or "hooks" on the vertebrae. If there is a crunch and squeak in the joints during movement, as if sand has been poured between them, for many patients the only cause of this condition is the notorious "salt deposition". can be determined based on an analysis of the reasons that caused it.
The term "osteochondrosis" comes from the Greek roots osteon - "bone" and chondr - "cartilage". The ending "-oz" means that the disease of bones and cartilage is not associated with inflammatory processes, has a degenerative-dystrophic nature, ie the basis of the disease is tissue malnutrition and, consequently, degeneration of its structure. Like all living tissues, the bone tissue of the vertebrae and the cartilaginous tissue of the intervertebral discs are constantly rearranged and self-renewed. Under the influence of regular physical activity they gain strength and elasticity, and in the absence of load the strength of the tissues decreases.
This is due to the peculiarities of nutrition and blood supply to bone and cartilage tissues. Adult discs do not have their own vessels; they receive nutrients and oxygen from neighboring tissues. Therefore, for proper nutrition of the discs, it is necessary to activate the blood circulation in the tissues around the discs. And this can only be achieved through intense muscular work.
According to its composition, the intervertebral disc can be divided into two parts: it is the gelatinous core that gives the disc elasticity, located in the center and the strong fibrous ring around it. Due to the deterioration of the nutrition of the intervertebral discs, the complex structure of the biopolymer compounds that make up the nucleus pulposus is destroyed. The moisture content in the gelatin core decreases and it becomes more brittle. When exposed to even small overloads, the gelatin core can break down into fragments. This leads to an even greater reduction in its elasticity. It also reduces the strength of the fibrous disc rings. All these factors form the basis and form the cause of osteochondrosis.
In order to restore the function of the spine, it is necessary to show signs of damage to the intervertebral disc, mobilization of the compensatory capabilities of the spine and the musculoskeletal system in general, and not the resorption of "salt deposits" or the elimination of "spikes". When performing an X-ray examination after the end of treatment, it can be seen that the vertebrae have not changed their shape. Marginal growths increase the area of the supporting surface of the body of the spine. By increasing the area, the specific pressure decreases, which makes it possible to compensate for the decrease in the strength and elasticity of the intervertebral disc.
Degenerative-dystrophic changes occurring in the spine are accompanied by calcification (calcification) of damaged discs, individual areas of joints, cartilage, capsules. This process can only be called salt deposition. Thus, this is not the cause of osteochondrosis, but only a consequence and the last stage of the above process.
The reverse development of structural changes in the spine is almost impossible. But minimizing them is a very real challenge. If no effort is made to keep the spine in the same condition as achieved with treatment, the pain may recur.
Clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis
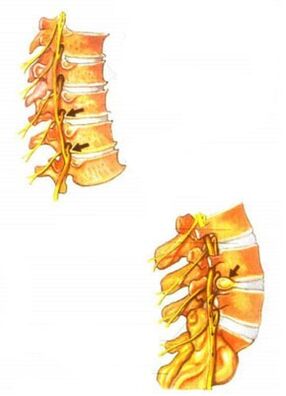
The clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis are very diverse. They depend on the stage of development of osteochondrosis. The main clinical symptoms of osteochondrosis appear when the pathological process spreads to the posterior part of the annular fibrosis and the posterior longitudinal ligament. Depending on the stage of degeneration of the intervertebral discs, irritation, compression or impaired conduction of the spinal cord roots, compression of the vessels or the spinal cord occur. Various neurological syndromes develop - reflex and compression.
The main cause of pain in osteochondrosis is the so-called irritation of the nerve root. In this case, circulatory disorders occur, edema occurs and in the future may develop fibrosis of the surrounding structures, which is accompanied by increased sensitivity of the roots to various influences (movements in the affected segment of the spine, etc. ).
Vascular disorders in osteochondrosis are often associated with impaired vasomotor innervation. Mechanical compression of blood vessels by osteophytes, for example in the cervical vertebrae, is also possible.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
One of the characteristics of spinal osteochondrosis, which worsens the process, is the very extensive symptoms. The disease can occur in completely different parts of the body. This may be pain or tingling in the limbs or disorders and pain in the internal organs. At the same time, a person often in no way associates pain in the heart, abnormalities in the functioning of the genitals, headache, pain and numbness of the legs with osteochondrosis and the spine in general, dealing with the "treatment" directly of the symptoms of osteochondrosis. using various types of painkillers, all kinds of advertised drugs, supplements, etc. But this time it only makes the situation worse. Osteochondrosis continues to develop and the methods of treatment used at best simply do not lead to significant improvement, except temporary relief ofpain, and in the worst case they can further harm the body.
Therefore, it is important to carefully analyze your condition and the changes that occur in it. You need to start moving in the right direction: consult a doctor in a timely manner, undergo the necessary diagnosis and only after determining the correct diagnosis begin treatment under the supervision of the attending physician.
The main symptoms of osteochondrosis include, in the first place, back pain and discomfort. At the same time, the pain can be periodic, unstable, sometimes appearing or disappearing. But the first feeling of discomfort or pain in the spine should make you think. The appearance of the first pains is a signal to at least pay attention to it, try to remember the reason why they appeared. This can be caused by lifting a heavy object, sudden movement, falling, etc.
Another symptom of osteochondrosis is the accompaniment of discomfort or back pain with pain and tingling in the limbs (arms or legs). The pain most often radiates to the left limb, ie the left arm or leg. In addition, the pain can occur in the heart, in the back and not only in the spine, but for example in the ribs, etc. In this case, it is especially important to pay attention to the nature of the change in pain depending onfrom the patient's actions by comparing the sensations of back pain with pain, for example in the leg. If the patient has been sitting for a long time and has pain or tingling in the foot, discomfort in the lower back and after a little warming up or walking the pain has disappeared, then this will be an indirect sign that determines lumbar osteochondrosis of the spine. The same picture can be with the neck and arm. In summary, we can say that the main symptoms of osteochondrosis include back pain and discomfort. In the case where these symptoms coincide with pain in other parts of the body, osteochondrosis can be complicated by a protruding, disc herniation with a pinched nerve.
In addition, I would like to draw attention to the fact that even at the onset of the first pain in the spine, it is necessary to pay special attention to this condition. Eventually, osteochondrosis may be mild or non-existent for a long time. At the same time, it will continue to develop successfully in the spine, leading to the degradation of an increasing number of discs. Therefore, a timely visit to the doctor will allow the diagnosis of osteochondrosis at an earlier stage, which will facilitate its treatment.
Osteochondrosis and salt deposition
Osteophytes or hook-like growths on the vertebrae appear to reduce the strain on the intervertebral discs. In this case, the appearance of osteophytes impairs the mobility of the intervertebral joints.
The common belief in everyday life that salt deposition is the main cause of osteochondrosis is wrong. Therefore, treating osteochondrosis with a salt-free diet is pointless.
The most common complaints of osteochondrosis of the spine
The most common complaints of osteochondrosis are as follows:
- Discomfort in different parts of the spine. The pain can range from minor, dull, pulling to severe, sometimes very intense and unbearable - with lumbago.
- Increased fatigue at work, both physical and mental.
- Sensory damage to the limbs and various parts of the body, coldness of the hands or feet.
- Pain radiating to the legs, along the nerve trunks.
- Pain radiating to the shoulder blade, shoulder, as well as pain in the neck and nape.
- A common companion of cervical osteochondrosis are headache, dizziness. Increased visual fatigue or decreased visual acuity is often observed.
- With the defeat of the lumbar-sacral region, disorders of the reproductive system are often observed - various sexual dysfunctions. Therefore, most men experience an increase in sexual potency after treatment. In women, the normal functioning of the lumbosacral area increases the likelihood of conception and contributes to a comfortable pregnancy.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
To diagnose osteochondrosis it is necessary to collect a history. In this case, it is crucial to identify the patient's complaints. Some symptoms of osteochondrosis are quite typical. Others, on the other hand, must be distinguished from the signs of other diseases. It is important that the nervous, vascular, trophic disorders that occur in osteochondrosis can simulate various diseases, such as angina pectoris, gastritis, gastric ulcer, acute surgical diseases of the abdominal organs. Therefore, in order to avoid misdiagnosis and subsequent prescribing of the wrong treatment, each symptom should be subjected to a detailed analysis.
When collecting a medical history, including the patient's complaints, the patient's current history, and life, the physician pays attention to his or her age, as osteochondrosis develops more frequently in the elderly and the evolution of symptoms from the time they occur until the patient leaves. to the doctor. Osteochondrosis is characterized by slow development, in which periods of exacerbation are periodically replaced by periods of remission. Additional examination methods are prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
X-ray examinations for osteochondrosis
The most accessible method for diagnosing osteochondrosis and at the same time quite informative is the X-ray examination. There are several types of X-ray method to diagnose this disease:
A simple X-ray of the spine is the simplest X-ray method to diagnose osteochondrosis. Its essence consists in obtaining an X-ray of the spine as a whole or of its individual segments. Most often, visual radiography is performed - based on the symptoms of the disease and the patient's complaints, the location of the spinal lesion is determined. On the X-ray image of the spinal segment affected by osteochondrosis, a decrease in the thickness (atrophy) of the intervertebral discs can be seen, which manifests itself in the form of a reduction in the space between the vertebrae, the appearance of bone growths on the vertebrae - osteophytes, partial dissolution -resorption of the bone tissue of the spinal body, change in the shape of the spinal segment, for example, smoothing of the lumbar lordosis.
Myelography is a more complex and dangerous diagnostic method. During such an examination, a certain amount of contrast fluid is injected into the spinal canal. The risk of this test method is the possibility of allergic reactions to the contrast agent or the risk of damage to the spinal cord during the puncture of the spinal canal. Thanks to myelography, the internal structure of the spinal canal can be determined. This method is particularly informative for the determination of spinal hernias.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are the most modern, but also the most expensive and difficult to diagnose osteochondrosis. These diagnostic methods are usually used when it is necessary to distinguish between osteochondrosis and other diseases of the spine that have similar symptoms, such as tumors of the spinal canal.
For a comprehensive assessment of the patient's condition, it is mandatory to conduct a neurological examination of the patient with osteochondrosis. Thanks to neurological consultation it is possible to clarify the location and degree of motor and sensory disorders.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
The clinic provides effective treatment for all forms of osteochondrosis. The treatment is performed on an outpatient basis. Treatment is based on a comprehensive program aimed at the rapid elimination of the underlying syndrome and the cause that causes suffering. The following methods can be used as part of the complex therapy:
- acupuncture;
- vacuum therapy;
- gentle techniques of manual therapy (post-isometric relaxation);
- laser therapy;
- pharmacopuncture;
- dry grip;
- magnetopuncture;
- electrical stimulation and other methods of treatment.
The average course of treatment is 10-15 sessions, and the elimination of acute pain syndrome is from 1 to 3 sessions.
The earlier the treatment starts, the better the result will be!
Is it complete to completely eliminate osteochondrosis?
This depends on the form of the disease, the severity, correctness and timeliness of treatment. Complete healing is possible only in the initial stages.
But it is possible to prevent exacerbations of osteochondrosis, not to feel pain for years. If a person has had osteochondrosis, but now does not feel discomfort, it does not mean that he passed without a trace. There may be changes in the spine.
The main task is to stop the development of the disease and to do everything possible so that some of the pathological changes in the spine disappear, the symptoms disappear or decrease (back pain, cold and tingling in the arms, legs, headache, etc. . n. ).



































